South African National Blood Service (SANBS)
Saving Lives Since 2001
and distribute blood to patients who need it due to trauma, surgery, or illness.
Blood Stock Levels
We need to maintain a blood stock level of 5 days for each blood group to
ensure sustained blood availability to patients in need.

(Donated blood is separated into red blood cells, plasma, and platelets – each of which can be given to a different patient).
About Us
We are an independent non-profit organisation and a leader in the discipline of blood transfusion.
We operate in eight out of nine provinces in South Africa (the Western Cape is serviced by the Western Cape Blood Services), and we also provide crucial support to other countries in the SADC region.
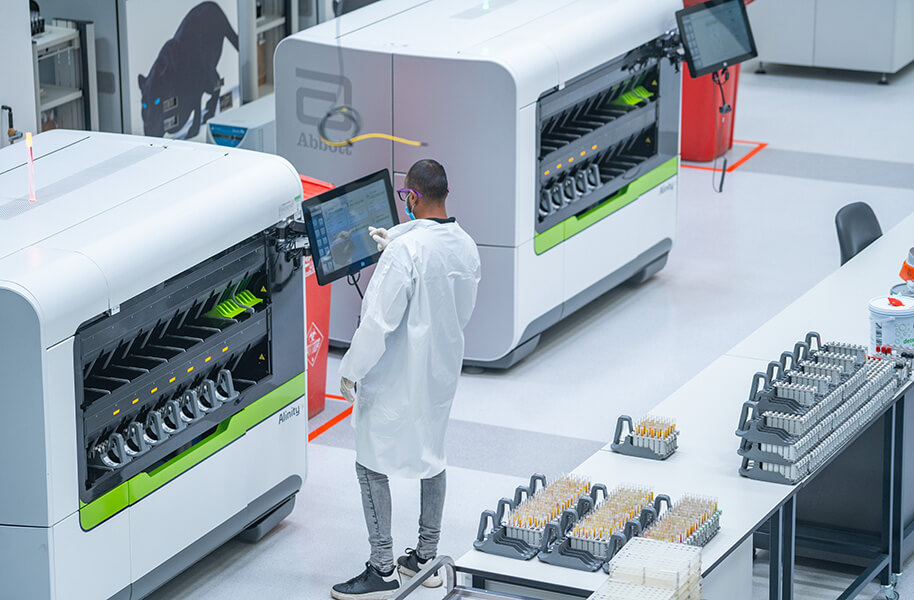
We supply over one million blood products annually and are rated among the top blood services in the world due to world-class testing and collection protocols which ensure that transfused blood is always of top quality.
The blood is separated into red blood cells, plasma, and platelets so each donation can save up to three lives.
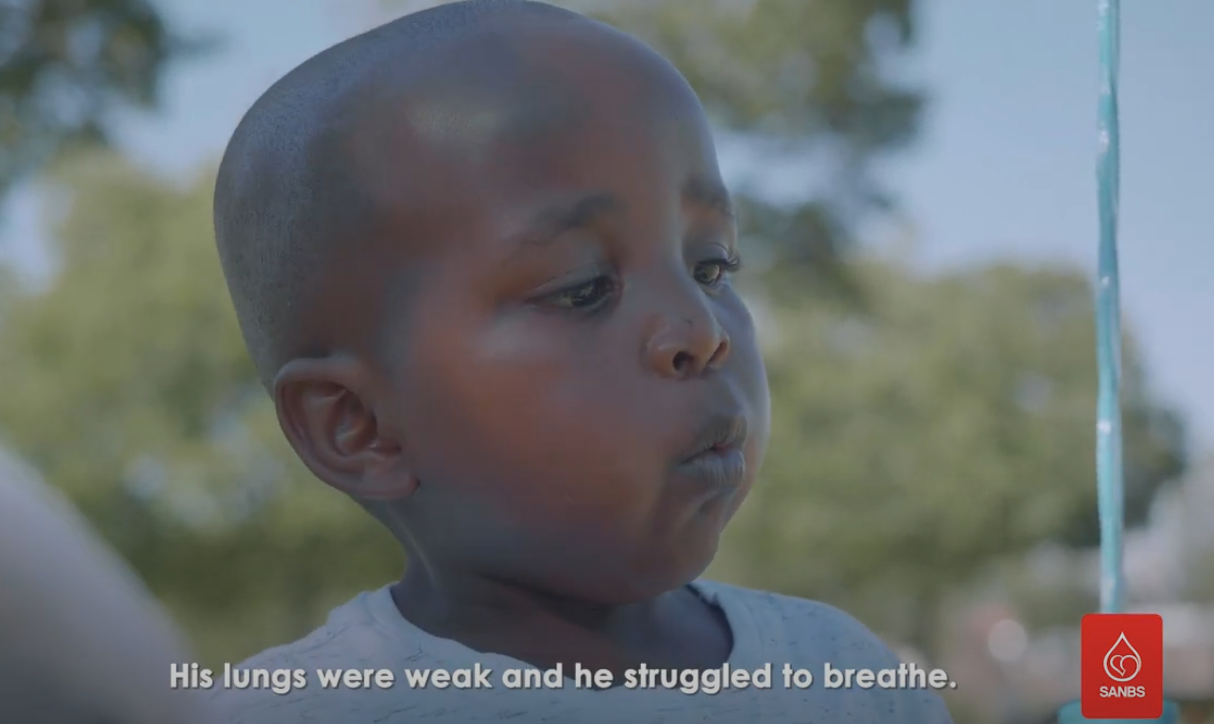
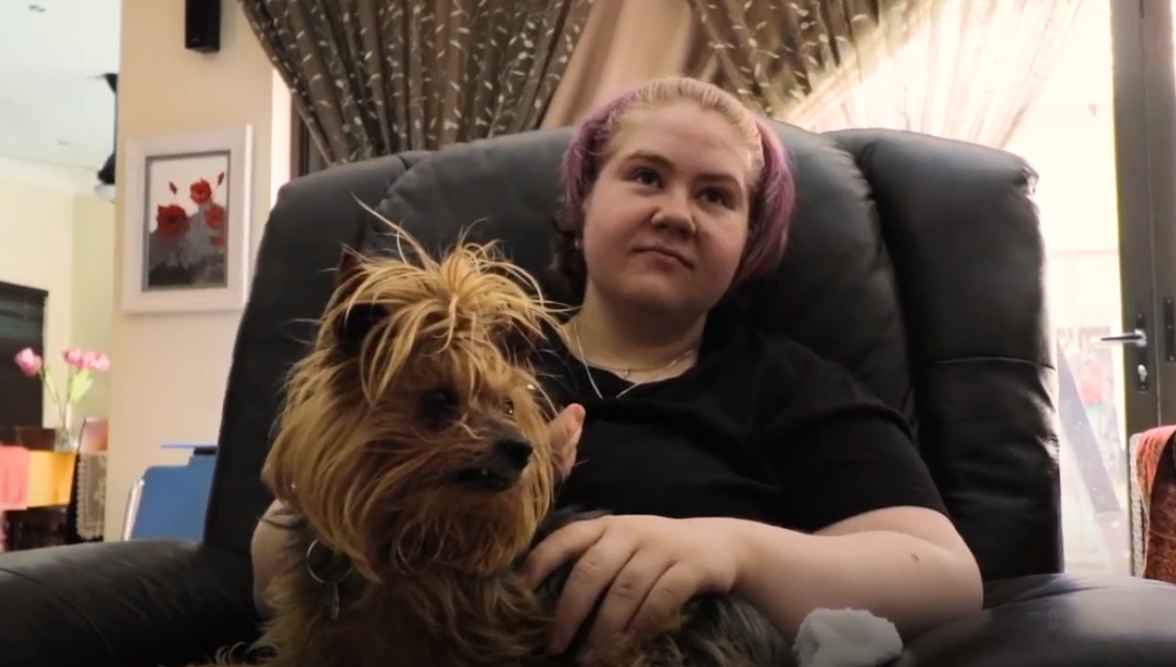
Read MoreRecipient Stories
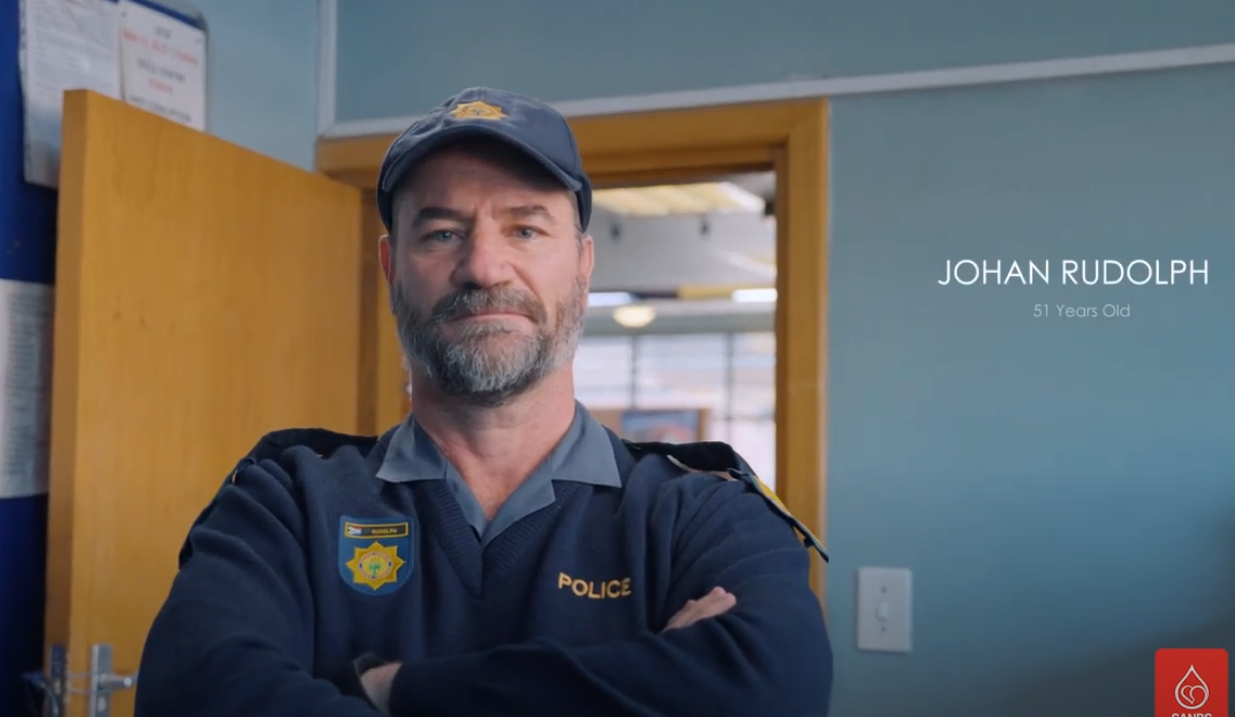
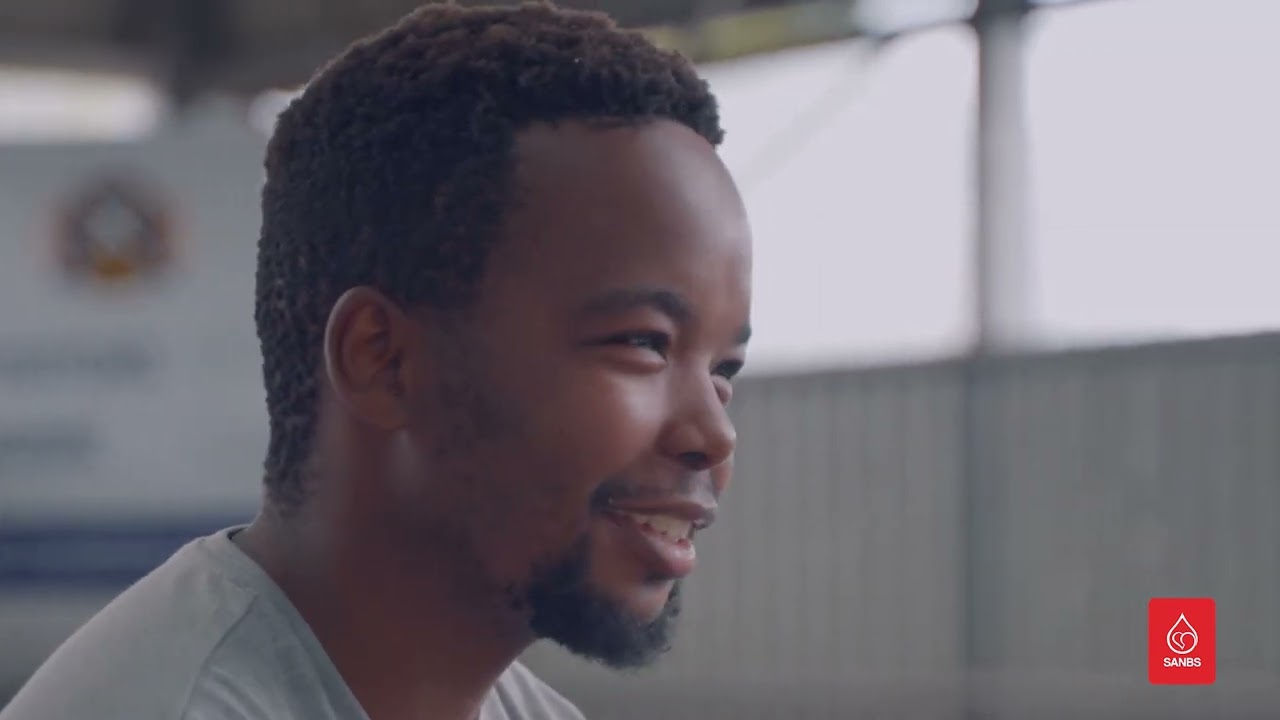
Seeing a practical example of someone who was saved by a blood transfusion makes it hit home in a different way though.
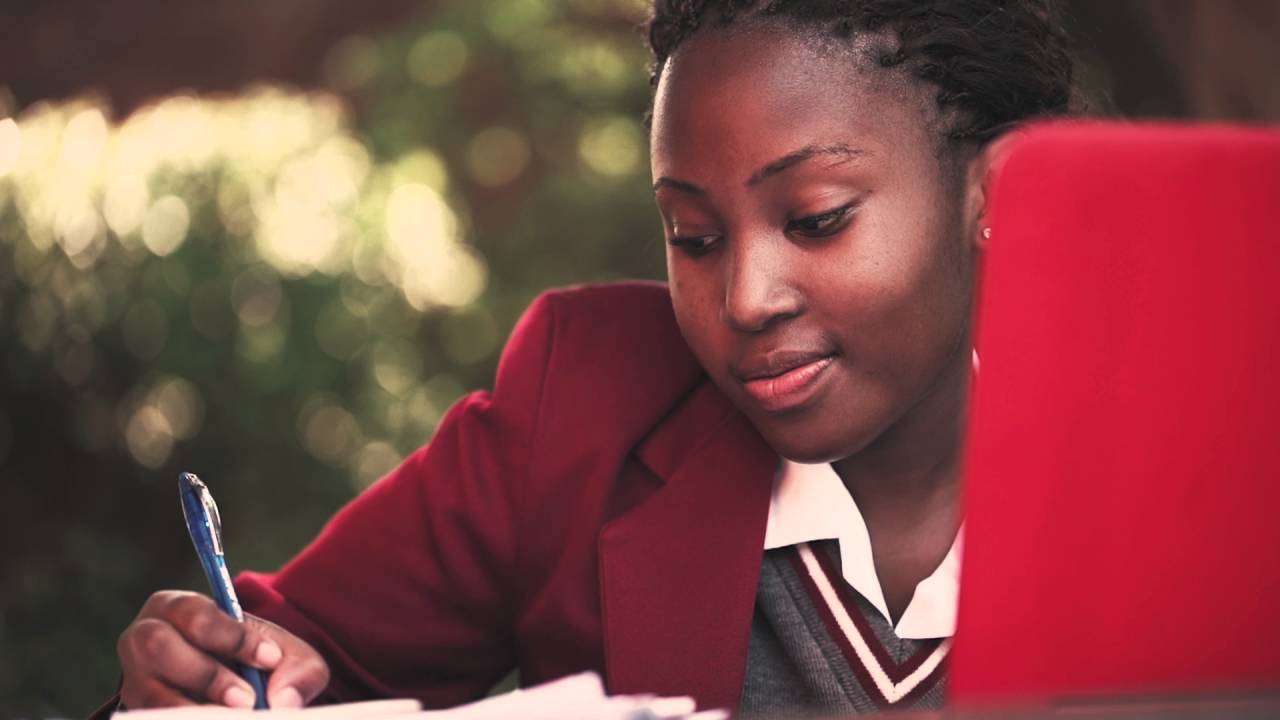
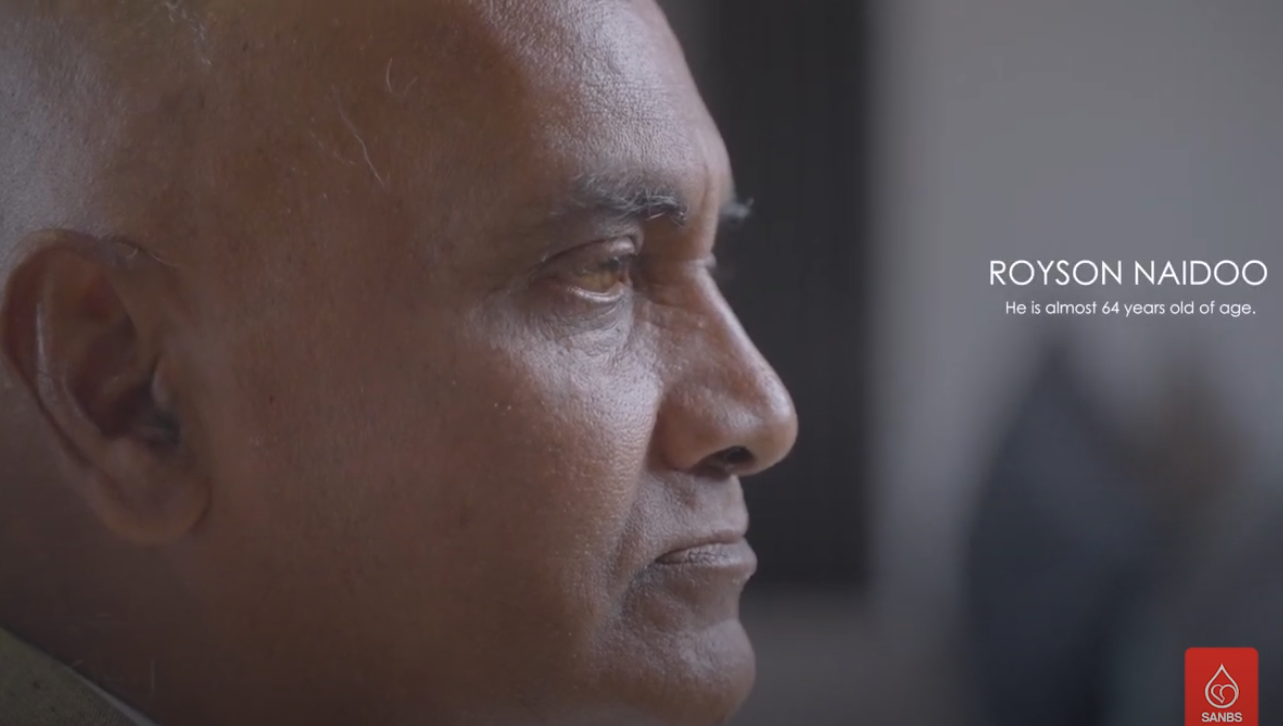
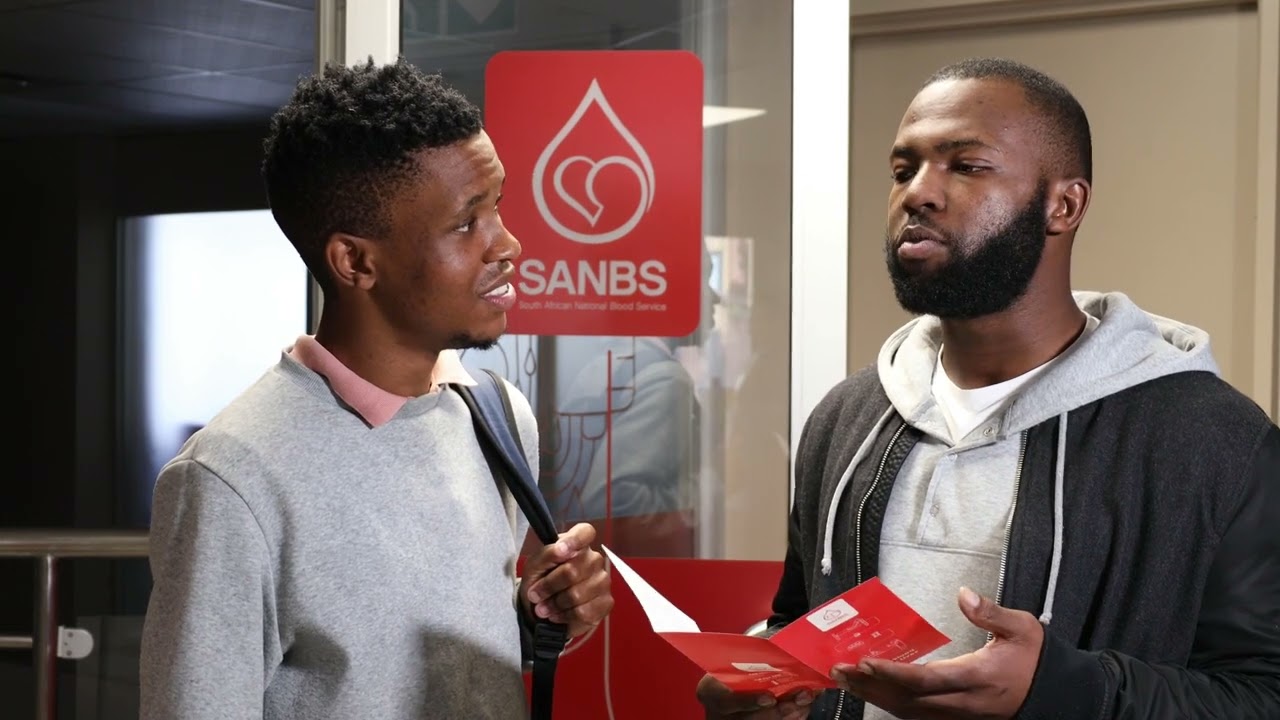
Donor Stories
We like to honour them wherever we can and tell their stories in the hope that it will inspire others to follow the example they set by becoming donors and regularly donating blood.
Latest News
Resource Links

We need to find new regular blood donors. Please contact us if you run, work for, are involved with, or know of a company, community, school, college, church, residential complex/estate, or any other place where we can run a blood drive.

If you are interested in partnering with SANBS, discover your next business opportunity by registering on our vendor portal to view the latest available tenders.

Get to know our board and executive team, whose inspiring stories and unwavering dedication have not only shaped SANBS into a trusted brand but also exemplify the commitment to excellence and innovation that drives our mission to save lives.

If you are interested in a career with us, please visit our jobs portal and apply for a current opening or upload your CV to be considered for future vacancies.
Organise a blood drive!
Help SANBS recruit new blood donors by organising a blood drive in your community,
office, school, college, church, or residential complex.